在 Solana 中,编写依赖时间流逝的测试用例颇具挑战。我们可能希望测试代码中某项操作是否在一天后发生,但不可能让测试真的等待一整天,否则测试将变得不切实际。LiteSVM 通过允许你瞬间将区块链时钟向前推进来解决这个问题,就像为本地测试提供了“时间旅行”功能。
为了展示其实际用法,我们将使用 Anchor 构建一个基础的 NFT 荷兰式拍卖(Dutch auction)。荷兰式拍卖从一个高价开始,价格随时间自动下降,直到有买家接受当前价格为止。这是一个典型的时间敏感型行为,而 LiteSVM 能极大简化对此类逻辑的测试。
LiteSVM 的工作方式类似于 Solana 的本地验证器(solana-test-validator),但它为测试环境提供了对本地区块链状态更精细的控制。它可用于 TypeScript 测试中,并能轻松测试基于时间的逻辑,例如拍卖或代币归属(vesting)。
如果你熟悉以太坊开发,LiteSVM 的时间操控能力类似于 Foundry 中的 vm.warp(用于推进区块时间戳),但专为 Solana 基于 slot 的架构量身定制。
本文将涵盖以下内容:
我们将创建一个用于 NFT 销售的荷兰式拍卖程序,包含创建拍卖和按递减价格购买 NFT 的函数;
我们将解释这些函数并为其编写测试;
最后,我们将使用 LiteSVM 将时间快进 15 分钟,无需真实等待即可测试价格衰减,并验证拍卖价格是否正确下降。
现在,让我们创建荷兰式拍卖程序。
创建荷兰式拍卖程序
如前所述,荷兰式拍卖起始价格高,并随时间下降,直至有买家接受。为确保交割,我们会将 NFT 锁定在一个由程序控制的保险库(即托管账户,escrow)中。这可以防止卖家撤回或重复出售 NFT,也让买家无需依赖卖家在付款后手动释放 NFT。一旦买家接受价格,程序便可原子化地完成交换。
该荷兰式拍卖程序仅包含两个函数:
initialize_auction 函数:创建所需账户,并将卖家的 NFT 存入由我们程序拥有的保险库账户;
buy 函数:允许买家以当前拍卖价格用 SOL 购买 NFT。
接下来,我们将创建以下账户:
Auction:由我们程序拥有的 PDA,用于存储拍卖详情,如起始价格、拍卖持续时间等;
Vault Authority:由我们程序拥有的 PDA,用于在成交时授权将 NFT 转移给买家。本文稍后的“为什么需要 Vault Authority PDA?”一节将详细说明;
Vault:一个关联代币账户(Associated Token Account),用于持有已存入的 NFT,其所有者为 Vault Authority PDA。
现在,创建一个名为 dutch-auction 的新 Anchor 项目,并在 programs/dutch-auction/Cargo.toml 文件中添加以下依赖项:
anchor-spl:用于 SPL 代币功能;
在 features 中启用 anchor-spl/idl-build,以便在生成的 IDL 文件中包含 SPL 类型。
[package] name = "dutch-auction" version = "0.1.0" description = "Created with Anchor" edition = "2021" [lib] crate-type = ["cdylib", "lib"] name = "dutch_auction" [features] default = [] cpi = ["no-entrypoint"] no-entrypoint = [] no-idl = [] no-log-ix-name = [] idl-build = ["anchor-lang/idl-build", "anchor-spl/idl-build"] [dependencies] anchor-lang = "0.30.1" anchor-spl = "0.30.1"
你可以运行 anchor build 来确认依赖项没有问题。
初始化拍卖程序
依赖项准备就绪后,将 programs/dutch-auction/src/lib.rs 中的程序代码替换为以下代码,其中包含 initialize_auction 函数,该函数执行以下操作:
初始化拍卖账户,并将拍卖详情和持续时间(以秒为单位)记录在该账户中;
将待拍卖的 NFT 从卖家的关联代币账户(ATA)转移至我们程序拥有的保险库(同样是一个 ATA)。
use anchor_lang::prelude::*;
use anchor_lang::solana_program::{program::invoke, system_instruction};
use anchor_spl::associated_token::AssociatedToken;
use anchor_spl::token::{self, Mint, Token, TokenAccount, Transfer};
declare_id!("GKP6La354ejTfqNDW4gdzC2mzNjnP6cMY1vtH6EN15zq");
#[program]
pub mod dutch_auction {
use super::*;
pub fn initialize_auction(
ctx: Context<InitializeAuction>,
starting_price: u64,
floor_price: u64,
duration: i64, // in seconds
) -> Result<()> {
// Initialize the auction account and set seller details
let auction = &mut ctx.accounts.auction;
auction.seller = ctx.accounts.seller.key();
auction.starting_price = starting_price;
auction.floor_price = floor_price;
auction.duration = duration;
auction.start_time = Clock::get()?.unix_timestamp;
auction.token_mint = ctx.accounts.mint.key();
// Move 1 token from seller ATA into vault escrow
let cpi_accounts = Transfer {
from: ctx.accounts.seller_ata.to_account_info(),
to: ctx.accounts.vault.to_account_info(),
authority: ctx.accounts.seller.to_account_info(),
};
let cpi_ctx = CpiContext::new(ctx.accounts.token_program.to_account_info(), cpi_accounts);
token::transfer(cpi_ctx, 1)?;
Ok(())
}
}
运行 anchor keys sync 以将程序 ID 替换为你自己的。
然后,在程序代码中添加 InitializeAuction 账户结构体以及 Auction 状态。
InitializeAuction 指定了拍卖初始化过程中涉及的以下账户:
auction:用于存储拍卖状态(起始价格、持续时间、卖家信息等)的账户;
seller:创建拍卖并签署交易的 NFT 所有者;
seller_ata:卖家持有待拍卖 NFT 的关联代币账户;
vault_auth:作为保险库账户权限方的 PDA(程序派生地址),使我们的程序能够控制 NFT 转移;
vault(托管账户):在拍卖期间持有卖家存入 NFT 的关联代币账户,由 Vault Authority PDA 拥有;
mint:代表被拍卖代币的 NFT 铸造账户。
#[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct InitializeAuction<'info> {
#[account(init, payer = seller, space = 8 + Auction::INIT_SPACE)]
pub auction: Account<'info, Auction>,
#[account(mut)]
pub seller: Signer<'info>,
#[account(
mut,
associated_token::mint = mint,
associated_token::authority = seller
)]
pub seller_ata: Account<'info, TokenAccount>,
/// CHECK: This is the PDA that will own the vault
#[account(
seeds = [b"vault", auction.key().as_ref()],
bump
)]
pub vault_auth: UncheckedAccount<'info>,
#[account(
init,
payer = seller,
associated_token::mint = mint,
associated_token::authority = vault_auth
)]
pub vault: Account<'info, TokenAccount>,
pub mint: Account<'info, Mint>,
pub token_program: Program<'info, Token>,
pub associated_token_program: Program<'info, AssociatedToken>,
pub system_program: Program<'info, System>,
}
#[account]
#[derive(InitSpace)]
pub struct Auction {
pub seller: Pubkey,
pub starting_price: u64,
pub floor_price: u64,
pub duration: i64,
pub start_time: i64,
pub token_mint: Pubkey,
pub sold: bool,
}
我们暂时不会测试此函数,待完整程序完成后统一测试。
接下来,我们添加用于购买拍卖代币的函数。
购买拍卖代币
在我们的拍卖设置中,NFT 在售出前一直存放在由程序控制的托管(保险库)账户中。购买拍卖代币意味着买家向卖家支付 lamports 以换取 NFT。
我们现在将添加一个函数,允许用户以当前荷兰式拍卖价格购买 NFT。该函数执行以下操作:
检查 NFT 是否已被售出;
获取当前时间,并验证拍卖是否处于活跃状态:若拍卖尚未开始,则返回 AuctionNotStarted 错误;若拍卖时间已结束,则返回 AuctionEnded 错误;
计算已过去的时间,并使用线性荷兰式拍卖公式计算当前价格;
确保买家拥有足够的 lamports;
将 lamports 从买家转移给卖家;
设置签名种子(signer seeds),使程序能够代表保险库签名;
将 NFT 从保险库转移至买家的关联代币账户。
pub fn buy(ctx: Context<Buy>) -> Result<()> {
// Check if the NFT is already sold
require!(
ctx.accounts.auction.sold == false,
AuctionError::NFTAlreadySold
);
let auction = &mut ctx.accounts.auction;
let now = Clock::get()?.unix_timestamp; // Get the current time from the clock sysvar
// Validate auction timing
require!(now >= auction.start_time, AuctionError::AuctionNotStarted);
require!(
now < auction.start_time + auction.duration,
AuctionError::AuctionEnded
);
// Calculate current price based on elapsed time (linear decay)
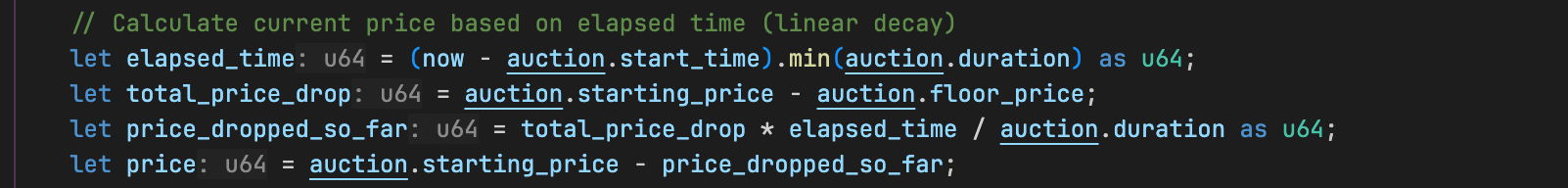
let elapsed_time = (now - auction.start_time).min(auction.duration) as u64;
let total_price_drop = auction.starting_price - auction.floor_price;
let price_dropped_so_far = total_price_drop * elapsed_time / auction.duration as u64;
let price = auction.starting_price - price_dropped_so_far;
// Verify funds and transfer payment
require!(
ctx.accounts.buyer.lamports() >= price,
AuctionError::InsufficientFunds
);
invoke(
&system_instruction::transfer(
&ctx.accounts.buyer.key(),
&ctx.accounts.seller.key(),
price,
),
&[
ctx.accounts.buyer.to_account_info(),
ctx.accounts.seller.to_account_info(),
ctx.accounts.system_program.to_account_info(),
],
)?;
// Transfer NFT to buyer
let auction_key = ctx.accounts.auction.key();
let vault_auth_bump = ctx.bumps.vault_auth;
let vault_signer_seeds = &[b"vault", auction_key.as_ref(), &[vault_auth_bump]]; // Signer seeds for the vault PDA
token::transfer(
CpiContext::new_with_signer(
ctx.accounts.token_program.to_account_info(),
Transfer {
from: ctx.accounts.vault.to_account_info(),
to: ctx.accounts.buyer_ata.to_account_info(),
authority: ctx.accounts.vault_auth.to_account_info(),
},
&[vault_signer_seeds],
),
1, // transfer 1 token (the auctioned NFT)
)?;
Ok(())
}
为什么需要 Vault Authority PDA?
我们使用一个保险库 ATA 来持有卖家存入的 NFT。我们需要一个 Vault Authority PDA,以便程序能在无需外部密钥对或签名者的情况下,为该 ATA 签署转账操作。
回想我们在《带有总供应量的代币销售》一文中展示的方法:我们将 mint PDA 设为其自身的权限方,使程序能自主铸造新代币。此处我们采用相同理念,但用于保险库 ATA,目的是赋予程序移动已有代币的能力。我们通过 ["vault", auction.key().as_ref()] 派生出 vault_auth,并将其设为 ATA 的权限方。
在 buy() 函数中,我们使用这些种子调用 CpiContext::new_with_signer。Solana 运行时会识别到我们的程序控制着 vault_auth,从而允许它为保险库 ATA 签名。这使得程序能自动将 NFT 转移给买家,无需任何外部签名者。
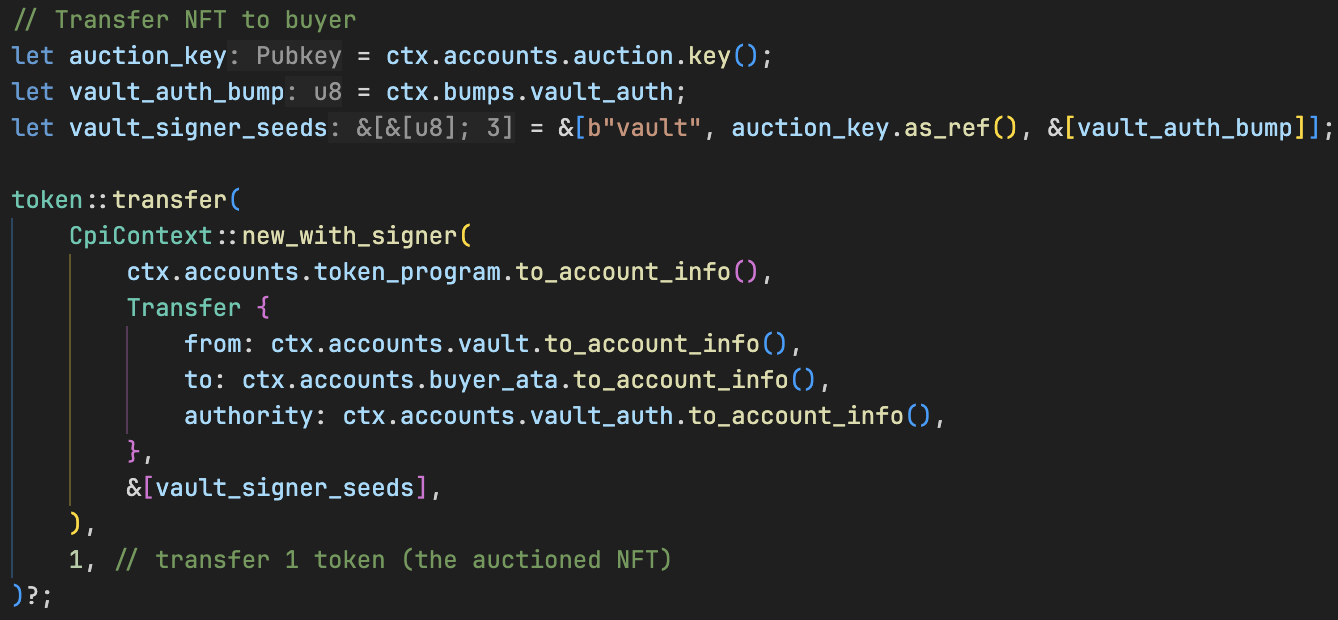
现在添加 Buy 账户结构体。Buy 结构体指定了拍卖程序中 NFT 购买过程所涉及的账户:
auction:包含拍卖详情和状态的账户;
seller:将收到 SOL 付款的原始 NFT 卖家;
buyer:以当前拍卖价格购买 NFT 的账户,同时也是交易签名者;
buyer_ata:将接收所购 NFT 的买家关联代币账户;
vault_auth:控制保险库并授权将 NFT 转移给买家的 PDA 权限方;
vault:由 vault_auth PDA 拥有的、持有托管 NFT 的保险库账户。
最后两个账户是我们在交互中使用的原生程序:
#[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct Buy<'info> {
#[account(mut, has_one = seller)] // ensure we pass the right auction account
pub auction: Account<'info, Auction>, // auction account
/// CHECK: seller account
#[account(mut)]
pub seller: AccountInfo<'info>, // seller account
#[account(mut)]
pub buyer: Signer<'info>, // buyer account
#[account(
mut,
associated_token::mint = auction.token_mint,
associated_token::authority = buyer
)]
pub buyer_ata: Account<'info, TokenAccount>, // Buyer's ATA
#[account(
mut,
seeds = [b"vault", auction.key().as_ref()],
bump
)]
/// CHECK: PDA authority for the vault
pub vault_auth: AccountInfo<'info>, // Vault authority PDA
#[account(
mut,
associated_token::mint = auction.token_mint,
associated_token::authority = vault_auth
)]
pub vault: Account<'info, TokenAccount>,
pub token_program: Program<'info, Token>, // SPL Token program
pub system_program: Program<'info, System>, // System program
}
Token Program(用于 NFT 转移);
System Program(用于 SOL 转移)。
添加 AuctionError 错误类型,我们在 buy 函数中使用它。
#[error_code]
pub enum AuctionError {
#[msg("Auction hasn't started")]
AuctionNotStarted,
#[msg("Buyer has insufficient funds")]
InsufficientFunds,
#[msg("Auction has ended")]
AuctionEnded,
#[msg("NFT is already sold")]
NFTAlreadySold,
}
至此,我们的程序已开发完成,接下来为其编写测试。
使用 LiteSVM 测试荷兰式拍卖程序
在荷兰式拍卖中,物品的价格会随时间递减。本次测试的目标是验证拍卖价格是否能随着时间正确衰减。为此,我们将使用 LiteSVM 将时间快进,并在该时间点记录价格的下降情况。
在真实的链上荷兰式拍卖中,我们必须实时等待才能观察到价格下降。而借助 LiteSVM,我们可以通过快进时间跳过等待。
我们将分步添加测试代码。首先,将 tests/dutch-auction.ts 中的程序测试替换为以下代码:
我们定义了一些测试常量。同时请注意本次测试所依赖的两个关键库:
litesvm:允许我们直接从 TypeScript 客户端启动一个本地 Solana 测试验证器,并提供对验证器时钟的控制能力,从而实现时间快进;
anchor-litesvm:将我们的 Anchor 项目与 LiteSVM 连接起来,使我们能在 LiteSVM 环境中测试 Anchor 程序。
import * as anchor from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { BN, Program } from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import {
ASSOCIATED_TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
createAssociatedTokenAccountInstruction,
createInitializeMintInstruction,
createMintToInstruction,
getAssociatedTokenAddress,
MINT_SIZE,
TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
} from "@solana/spl-token";
import {
Keypair,
LAMPORTS_PER_SOL,
PublicKey,
SystemProgram,
Transaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
import { fromWorkspace, LiteSVMProvider } from "anchor-litesvm";
import { assert } from "chai";
import { Clock, LiteSVM } from "litesvm";
import { DutchAuction } from "../target/types/dutch_auction";
// Constants
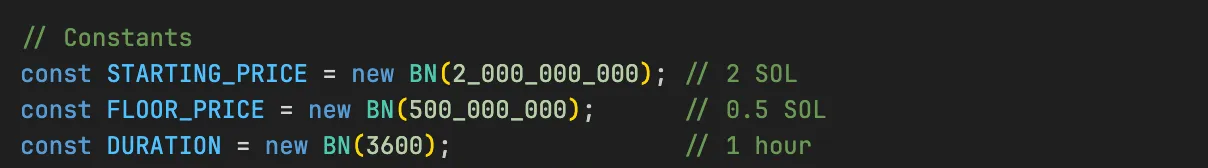
const STARTING_PRICE = new BN(2_000_000_000); // 2 SOL
const FLOOR_PRICE = new BN(500_000_000); // 0.5 SOL
const DURATION = new BN(3600); // 1 hour
使用以下命令安装测试依赖项:
npm install anchor-litesvm litesvm @solana/spl-token
添加 describe 块。我们在此处仅声明测试账户和变量(稍后会详细说明)。
接下来,在 describe 块内添加 before 测试块:
describe("dutch-auction", () => {
// Define our test variables
let svm: LiteSVM;
let provider: LiteSVMProvider;
let program: Program<DutchAuction>;
// Define our test accounts
const seller = Keypair.generate();
const buyer = Keypair.generate();
let auctionAccount: Keypair;
let mintKp: Keypair;
let sellerAta: PublicKey;
let buyerAta: PublicKey;
let vaultAuth: PublicKey;
let vault: PublicKey;
});
我们在该块中完成 LiteSVM 和账户的设置,具体包括:
初始化 LiteSVM 测试环境;
向测试账户(买家和卖家)空投 SOL;
使用 @solana/spl-token 库为买家和卖家创建代币铸造账户(mint)及关联代币账户(ATA);
向卖家铸造 NFT;
创建拍卖账户和保险库权限方 PDA;
使用起始参数初始化拍卖。
本测试中构造交易的方式与以往略有不同,其原因将在代码块后说明。
before(async () => {
// Initialize LiteSVM from the workspace and add SPL/Builtins/Sysvars
svm = fromWorkspace("./").withSplPrograms().withBuiltins().withSysvars();
provider = new LiteSVMProvider(svm);
anchor.setProvider(provider);
program = anchor.workspace.DutchAuction;
// Airdrop funds to seller and buyer
svm.airdrop(seller.publicKey, BigInt(10 * LAMPORTS_PER_SOL)); // Airdrop 10 SOL to seller
svm.airdrop(buyer.publicKey, BigInt(10 * LAMPORTS_PER_SOL)); // Airdrop 10 SOL to buyer
// Create NFT mint (0 decimals) with seller as mint authority
mintKp = Keypair.generate();
const LAMPORTS_FOR_MINT = 1_000_000_000; // sufficient for rent in tests
const createMintIx = SystemProgram.createAccount({
fromPubkey: seller.publicKey,
newAccountPubkey: mintKp.publicKey,
lamports: LAMPORTS_FOR_MINT,
space: MINT_SIZE,
programId: TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
});
const initMintIx = createInitializeMintInstruction(
mintKp.publicKey,
0, // decimals
seller.publicKey, // mint authority
null // freeze authority
);
const mintTx = new Transaction().add(createMintIx, initMintIx);
mintTx.recentBlockhash = svm.latestBlockhash();
mintTx.feePayer = seller.publicKey;
mintTx.sign(seller, mintKp);
svm.sendTransaction(mintTx);
// Create ATA for the seller
sellerAta = await getAssociatedTokenAddress(mintKp.publicKey, seller.publicKey);
const createSellerAtaIx = createAssociatedTokenAccountInstruction(
seller.publicKey,
sellerAta,
seller.publicKey,
mintKp.publicKey
);
const sellerAtaTx = new Transaction().add(createSellerAtaIx);
sellerAtaTx.recentBlockhash = svm.latestBlockhash();
sellerAtaTx.feePayer = seller.publicKey;
sellerAtaTx.sign(seller);
svm.sendTransaction(sellerAtaTx);
// Create ATA for the buyer
buyerAta = await getAssociatedTokenAddress(mintKp.publicKey, buyer.publicKey);
const createBuyerAtaIx = createAssociatedTokenAccountInstruction(
buyer.publicKey,
buyerAta,
buyer.publicKey,
mintKp.publicKey
);
const buyerAtaTx = new Transaction().add(createBuyerAtaIx);
buyerAtaTx.recentBlockhash = svm.latestBlockhash();
buyerAtaTx.feePayer = buyer.publicKey;
buyerAtaTx.sign(buyer);
svm.sendTransaction(buyerAtaTx);
// Mint 1 token to seller's ATA
const mintToIx = createMintToInstruction(
mintKp.publicKey,
sellerAta,
seller.publicKey,
BigInt(1)
);
const mintToTx = new Transaction().add(mintToIx);
mintToTx.recentBlockhash = svm.latestBlockhash();
mintToTx.feePayer = seller.publicKey;
mintToTx.sign(seller);
svm.sendTransaction(mintToTx);
// Find PDA for vault authority and associated token account
[vaultAuth] = PublicKey.findProgramAddressSync(
[Buffer.from("vault"), auctionAccount.publicKey.toBuffer()],
program.programId
);
vault = await getAssociatedTokenAddress(
mintKp.publicKey,
vaultAuth,
true
);
// Initialize the auction (moves 1 token from seller ATA to vault)
await program.methods
.initializeAuction(STARTING_PRICE, FLOOR_PRICE, DURATION)
.accounts({
auction: auctionAccount.publicKey,
seller: seller.publicKey,
sellerAta,
vaultAuth,
vault,
mint: mintKp.publicKey,
tokenProgram: TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
associatedTokenProgram: ASSOCIATED_TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
systemProgram: SystemProgram.programId,
})
.signers([seller, auctionAccount])
.rpc();
});
上述测试中使用了一些 LiteSVM 的特性和方法,我们稍后会详细讨论。
接下来,添加以下测试块。该块仅用于断言拍卖程序已在 before 块中正确初始化。
it("initializes auction state correctly", async () => {
const auction = await program.account.auction.fetch(auctionAccount.publicKey);
assert.ok(auction.seller.equals(seller.publicKey));
assert.equal(auction.startingPrice.toNumber(), STARTING_PRICE.toNumber());
assert.equal(auction.floorPrice.toNumber(), FLOOR_PRICE.toNumber());
assert.equal(auction.tokenMint.toBase58(), mintKp.publicKey.toBase58());
// Seller's NFT should have moved to vault during initialization
const vaultAcc = svm.getAccount(vault);
assert.isNotNull(vaultAcc, "Vault ATA must exist");
});
在运行测试之前,让我们先梳理一下 LiteSVM 相关库及其用法。
如下图所示,我们在测试中声明了两个主要变量:

svm:来自 litesvm 库的 LiteSVM 实例。它类似于一个可控制的本地 Solana 测试验证器,包括对其时钟进行时间快进的能力;
provider:来自 anchor-litesvm 库的 LiteSVMProvider。它行为类似标准的 Anchor provider,但专为与 LiteSVM 协同工作而设计,使我们能够在支持时间快进的环境中运行测试。
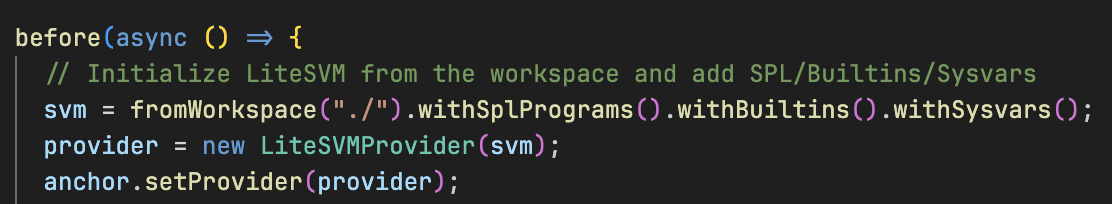
如上图所示,我们通过初始化 LiteSVM、创建 LiteSVM provider 并配置 Anchor 使用该 provider 来搭建测试环境。
具体分解如下:
fromWorkspace("./")(来自 litesvm 库)从当前目录创建一个 LiteSVM 实例,告知 LiteSVM 在何处查找项目文件。随后我们对该实例链式调用多个方法:
此方法链返回一个完全配置好的 LiteSVM 对象,赋值给 svm。
.withSplPrograms():添加 SPL 代币程序,使测试中支持代币功能;
.withBuiltins():添加内置程序,提供对原生 Solana 程序的访问;
.withSysvars():添加系统变量(sysvars),使我们能访问 Solana 系统信息(如时钟)。
new LiteSVMProvider(svm)(来自 anchor-litesvm 库)创建一个与 LiteSVM 兼容的 provider,同时遵循 Anchor 所期望的接口;
anchor.setProvider(provider) 告知 Anchor 使用我们这个兼容 LiteSVM 的 provider。
完成此设置后,我们即可使用 LiteSVM provider 进行时间快进操作。
现在我们已搭建好测试环境,接下来说明如何在 LiteSVM 中手动创建 SPL 代币和关联代币账户(ATAs)。与常规做法不同——通常我们会使用 @solana/spl-token 库中的 createMint() 和 createAssociatedTokenAccount() 等辅助函数——在 LiteSVM 中,我们需要手动构建这些指令,并通过 svm.sendTransaction() 执行。
因为 @solana/spl-token 的辅助函数与 LiteSVM 的测试环境并非完全兼容。
下面逐步说明我们如何为拍卖创建 NFT。
步骤 1:创建 Mint 账户
首先,我们创建 mint 账户。
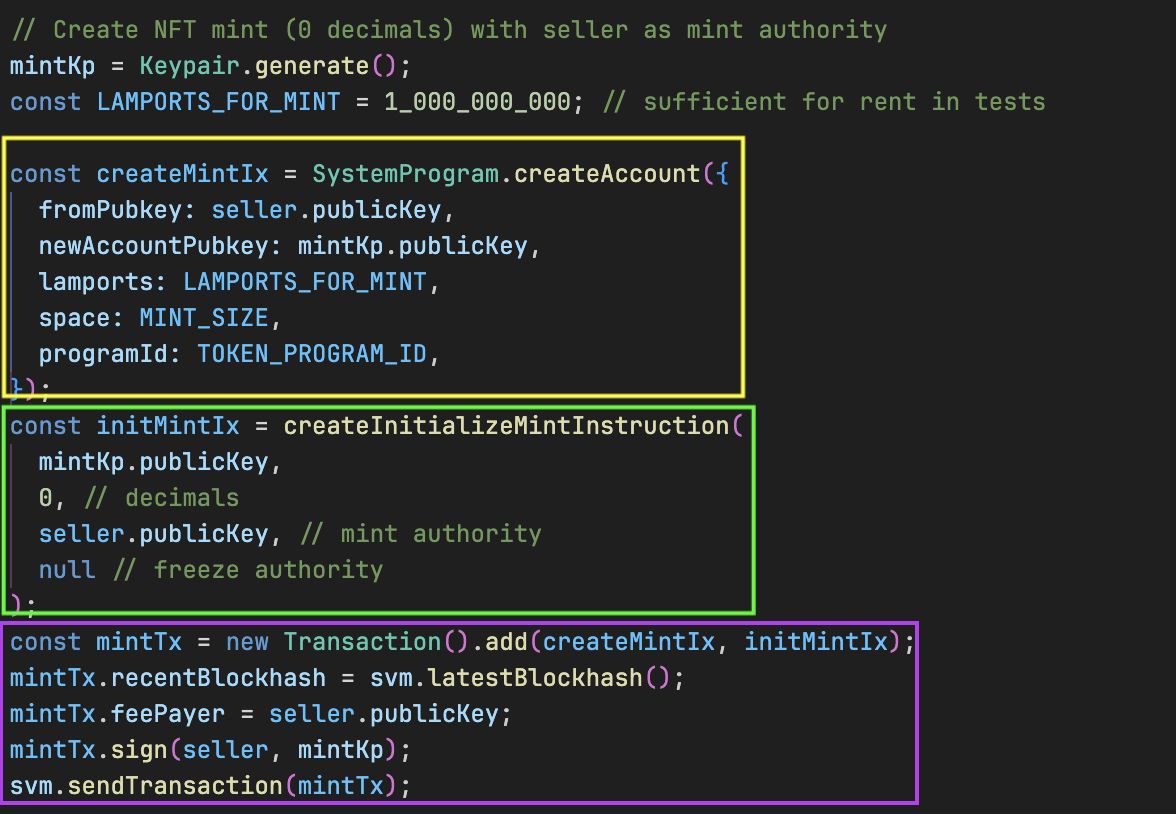
如上图所示,具体过程如下:
创建账户:使用 SystemProgram.createAccount()(从 @solana/web3.js 导入)在链上分配空间,并将所有权指定给 Token Program。这是为了符合 SPL 代币标准——所有代币 mint 账户必须由 Token Program 拥有才有效;
初始化为 mint:使用 createInitializeMintInstruction()(从 @solana/spl-token 导入)将该原始账户初始化为一个具有 0 位小数的合法代币 mint。这是因为 Solana 的 NFT 标准要求小数位为 0,以确保不可分割性;
执行:我们构建交易,设置 blockhash 和手续费支付者,签名后通过 svm.sendTransaction() 发送给 LiteSVM 实例。这与向 Solana 区块链发送交易类似,但发生在本地 LiteSVM 环境中。
步骤 2:创建代币账户
接下来,我们为卖家和买家创建关联代币账户(ATAs)。我们使用 getAssociatedTokenAddress()(从 @solana/spl-token 导入)推导账户地址,并使用 createAssociatedTokenAccountInstruction()(同样来自 @solana/spl-token)生成用于初始化这些账户的指令。
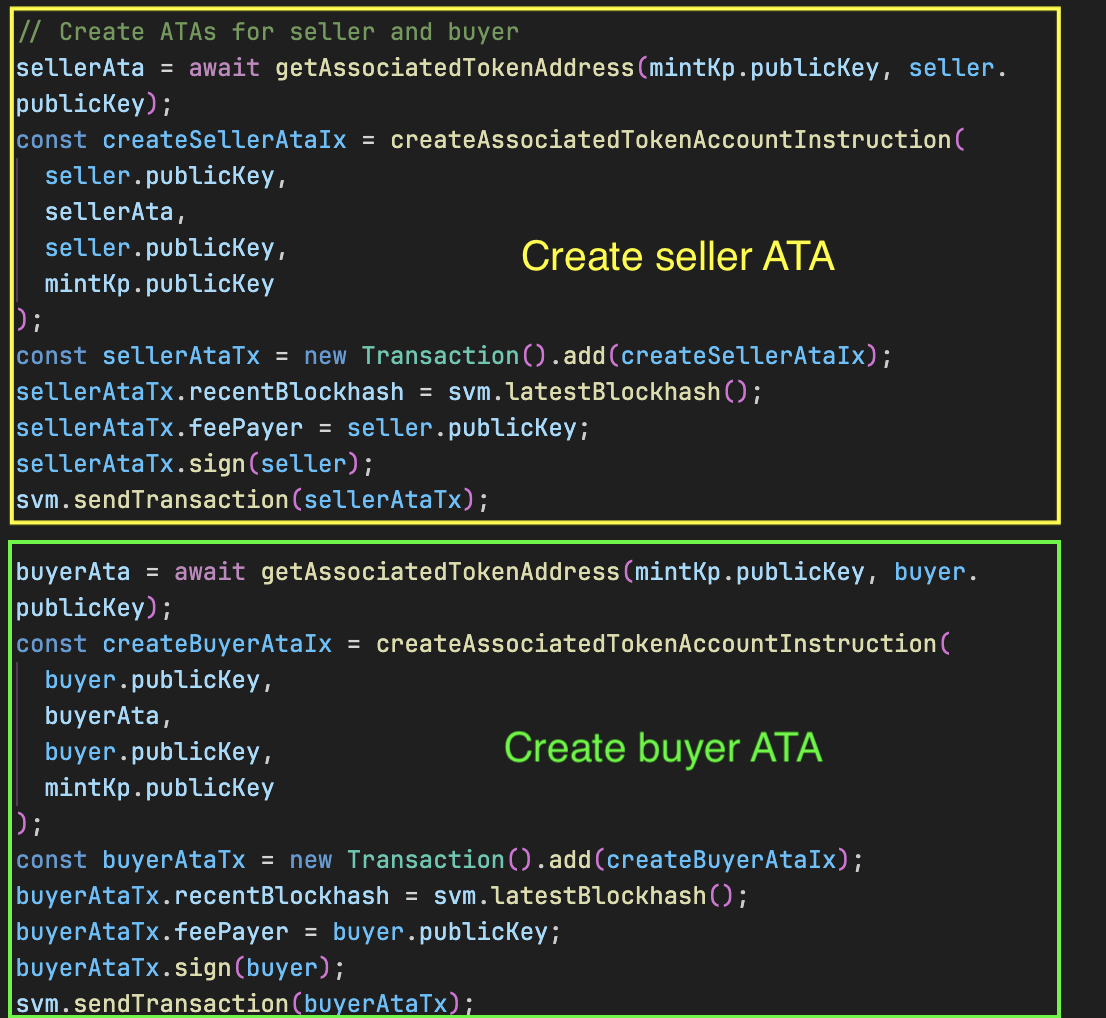
这些 ATAs 将在拍卖前后分别持有卖家和买家的 NFT。
由于 LiteSVM 不提供代币操作的辅助函数,我们沿用“手动构建交易 → 签名 → 通过 svm.sendTransaction() 发送”的模式。
现在我们已设置好测试环境并创建了必要的代币账户,可以开始实现核心目标:模拟时间流逝,并验证拍卖价格是否随时间正确下降。
我们将快进时钟,并在特定时间点调用程序中的 buy 函数,以确认价格符合预期衰减值。
现在添加以下测试块。在此测试中,我们希望验证随着时间推移,拍卖价格确实正确下降。具体操作如下:
获取链上拍卖数据,提取关键参数(起始时间、持续时间等);
计算拍卖进行到 15 分钟时应有的价格(即总时长 60 分钟的 25%);
使用 LiteSVM 将 Solana 时钟快进 15 分钟;
在购买前检查买家的 SOL 余额;
调用 buy 函数,模拟按当前价格购买;
检查买家的新余额,并与之前余额相减,得出实际支付金额;
验证支付金额是否等于预期价格(1.625 SOL)。
it("executes buy at 25% time with expected price and transfers NFT", async () => {
const auction = await program.account.auction.fetch(auctionAccount.publicKey);
const startTime = auction.startTime.toNumber();
const duration = auction.duration.toNumber();
const quarterTime = startTime + Math.floor(duration / 4);
// Warp clock to 25% into the auction
const c = svm.getClock();
svm.setClock(
new Clock(c.slot, c.epochStartTimestamp, c.epoch, c.leaderScheduleEpoch, BigInt(quarterTime))
);
// Check buyer's lamports before purchase
const balanceBefore = svm.getBalance(buyer.publicKey)!;
// Execute the buy transaction
console.log('Executing buy transaction...');
await program.methods
.buy()
.accounts({
auction: auctionAccount.publicKey,
seller: seller.publicKey,
buyer: buyer.publicKey,
buyerAta,
vaultAuth,
vault,
tokenProgram: TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
systemProgram: SystemProgram.programId,
})
.signers([buyer])
.rpc();
// Check buyer's lamports after purchase
const balanceAfter = svm.getBalance(buyer.publicKey)!;
// Calculate the price paid and log it
const pricePaid = Number(balanceBefore - balanceAfter);
console.log(`Actual price paid: ${lamportsToSol(pricePaid)}`);
// Expected price at 25% through the auction duration:
// Starting price - ((Starting price - Floor price) * 0.25) =
// 2 SOL - ((2 SOL - 0.5 SOL) * 0.25) = 1.625 SOL = 1,625,000,000 lamports
const expectedPriceAt25Percent = 1_625_000_000;
// Assert that the price paid is equal to the expected price
assert.equal(
pricePaid,
expectedPriceAt25Percent,
"Buyer should pay the 25% elapsed linear price"
);
// Verify buyer received the NFT (amount stored at bytes 64..72)
const buyerAtaAcc = svm.getAccount(buyerAta)!;
// Read the token amount as u64 (little-endian) from offset 64
const amount = Number(Buffer.from(buyerAtaAcc.data).readBigUInt64LE(64));
assert.equal(amount, 1, "Buyer ATA should now contain 1 token");
});
此前,我们在测试中初始化拍卖时设定了起始价格为 2 SOL,持续时间为 60 分钟。
根据程序 buy 函数中使用的公式,经过 15 分钟(即拍卖总时长的 25%),价格应下降 25%,计算结果为 1.625 SOL,这正是我们测试中预期的价格。
如上所述的测试块中,我们使用 svm.setClock 覆盖 Clock 系统变量(sysvar),以模拟拍卖过程中的更晚时间点。
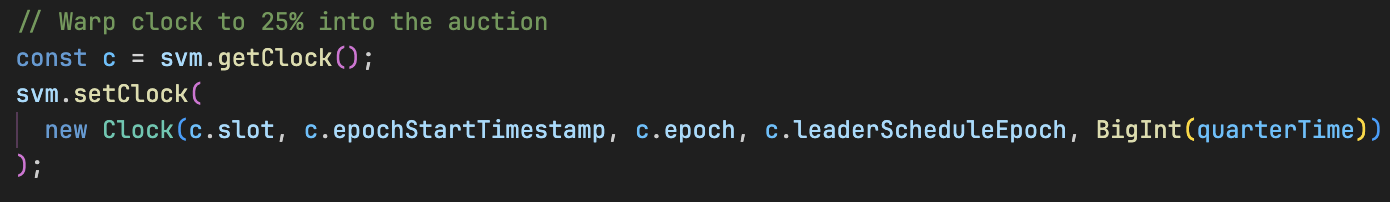
该方法接收一个 Clock 对象(从 litesvm 导入),我们将 unixTimestamp 设置为拍卖开始时间之后 15 分钟(由 quarterTime 定义)。这使我们无需真实等待即可测试价格衰减。
这一切之所以可行,都得益于我们在 before 块中完成的 LiteSVM 初始化和账户创建。
现在所有测试均已就位,我们可以像运行普通 Anchor 程序测试一样,通过 anchor test 命令执行测试,且测试能够顺利通过。
总结
在本教程中,我们实现了一个荷兰式拍卖,其中代币价格随时间线性递减,并编写了测试来验证其逻辑。
我们使用 litesvm(以及 anchor-litesvm)创建了一个本地测试环境,能够在其中快进时间。这使我们无需实际等待即可模拟 15 分钟的流逝,并确认拍卖价格从 2 SOL 正确下降至 1.625 SOL(即拍卖进行到 25% 时的预期价格)。
通过覆盖 Clock 系统变量(sysvar)并利用 LiteSVM 提供的 API,我们得以以确定性的方式测试基于时间的逻辑。
原文:https://rareskills.io/post/litesvm#testing-the-dutch-auction-program-with-litesvm
免责声明:本文为c2e Labs的第三方内容,仅供信息分享与传播之目的,不代表我们的立场或观点且不构成任何投资及应用建议。版权归原作者或来源方所有,如内容或素材有所争议请和我们取得联系。